

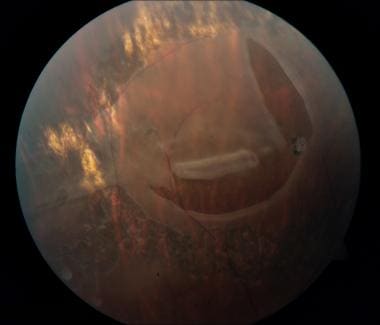
Younger myopic patients who have lattice degeneration with round holes need regular follow-up visits, because they can develop small, localized retinal detachments, which occasionally slowly enlarge to become clinical retinal detachments. Lattice degeneration can cause RRD by two mechanisms, including either round holes without PVD or tractional tears associated with PVD. The early diagnosis of a retinal detachment is also important because the rate of successful reattachment is higher and the visual results are better if detachment spares the macula.1,2 Successful treatment allows patients to maintain their abilities to read, work, drive, care for themselves, and enjoy a better quality of life.3 Lattice Degeneration
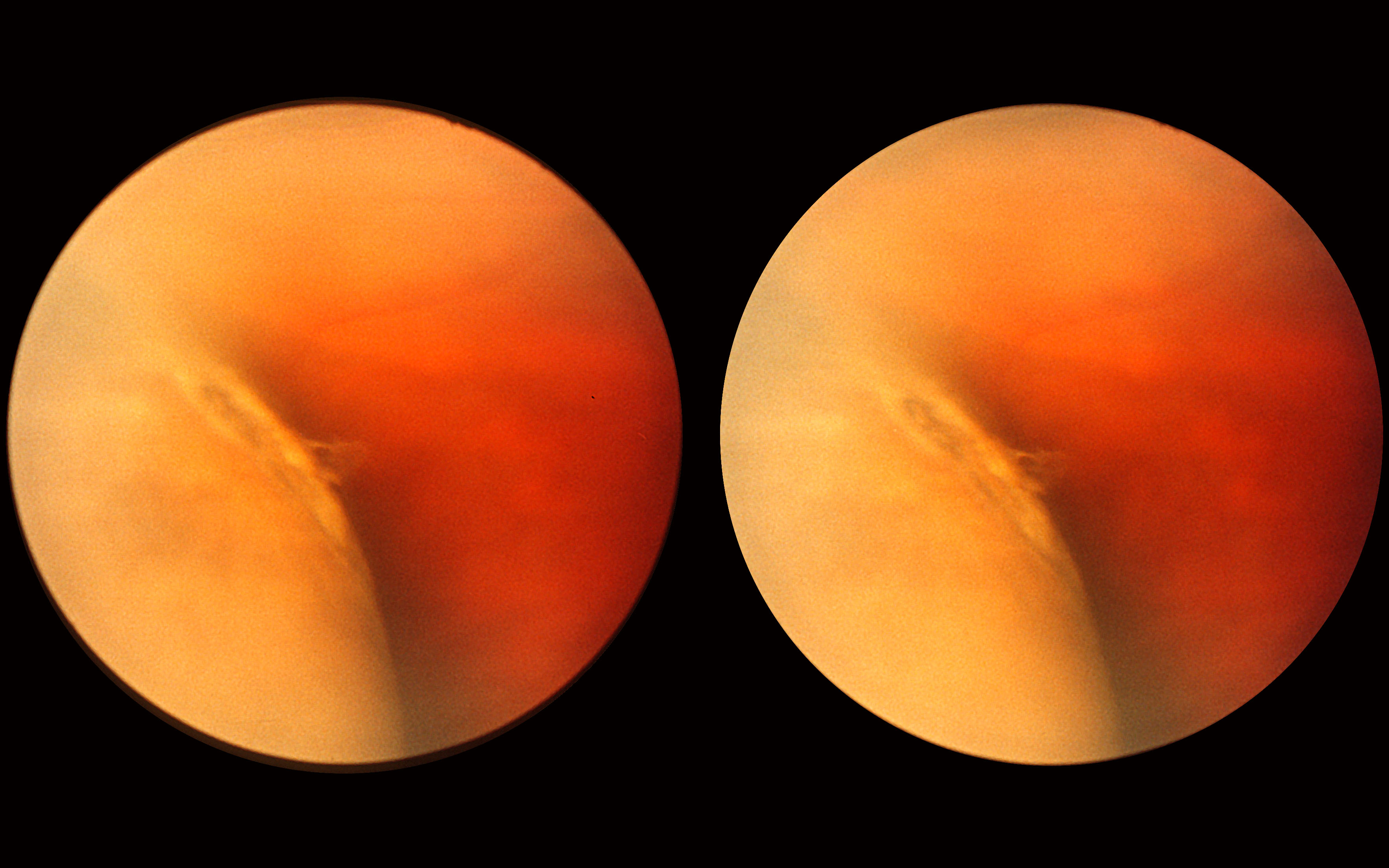
The treatment of breaks/lattices before a significant detachment has occurred usually prevents progression, is uncomplicated and results in excellent vision. Currently, more than 95% of RRDs can be successfully repaired, although more than one procedure may be required. Because spontaneous reattachment is exceedingly rare, nearly all patients with asymptomatic RRD will progressively lose vision unless the detachment is repaired. Precursors to retinal detachments are PVD, symptomatic retinal breaks, asymptomatic retinal breaks, lattice degeneration, and cystic and zonular traction retinal tufts. Natural history of precursors to rhegmatogenous retinal detachment
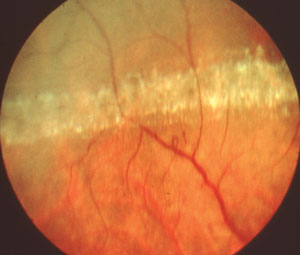
Manage patients at high risk of developing retinal detachmentĮducate high-risk patients about symptoms of PVD, retinal breaks, and retinal detachments and about the need for periodic follow-up. It usually takes 10 to 20 minutes to complete the procedure after which the patient may immediately go home.GOALS of identifying the patients with risk of RD are:Įxamine patients with symptoms of acute PVD to detect and treat significant retinal breaks It is aOPD based non-invasive procedure and does not require hospital administration. The laser is used to cauterize tiny vessels in the retina to repair holes and reduce the chances of detachment occurring. In laser photocoagulation, a laser is directed at the retina of the eye. Laser photocoagulation of retinal tears is the most common prophylactic treatment used for lattice eye degeneration. If these symptoms suddenly appear with no warning, they may indicate retinal detachment, and treatment from an Eye Doctor ( Ophthalmologist ) should be sought.įor people with lattice degeneration, prophylactic treatment may be needed to prevent complications.like retinal detachment. Floaters are tiny black spots which float in the field of vision. When retinal detachment occurs, the patient is likely to experience floaters and white flashes in their field of vision. The most common complication of lattice degeneration is retinal detachment. Often, when symptoms are noticed they are symptoms of a complication rather than of the disease itself. Lattice degeneration does not generally present any easily recognizable symptoms. Diseased eyes have vascular deficiencies, meaning the network of vessels which supplies blood to the retina is underdeveloped. Although multiple theories have been suggested about the cause of this disease, the factors which lead to lattice eye degeneration remain unknown.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
